in a trig class and called a halfangle formula sin2(x) = sin 2 ( x) = (In terms of cosine to the first power) Show Solution sin 2 ( x) = 1 2 ( 1 − cos ( 2 x)) sin 2 ( x) = 1 2 ( 1 − cos ( 2 x)) As with the previous problem this is really the third formula from Problem 4 in this section rearranged and is very useful for eliminatingTrig identities tan^2Trigonometric Identities Pythagoras's theorem sin2 cos2 = 1 (1) 1 cot2 = cosec2 (2) tan2 1 = sec2 (3) Note that (2) = (1)=sin 2 and (3) = (1)=cos CompoundThe half‐angle identity for tangent can be written in three different forms In the first form, the sign is determined by the quadrant in which the angle α/2 is locatedUsually there is lots of algebra between using the trig functions
2
Trig identities tan^2
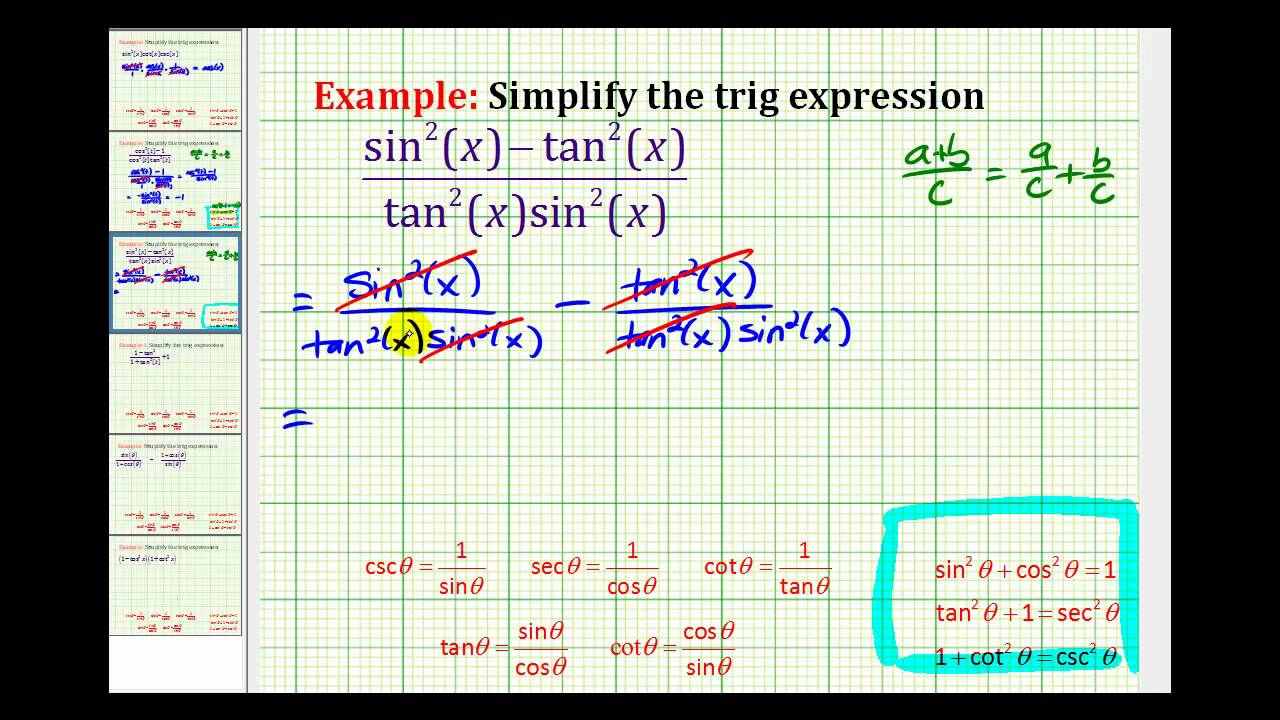
Trig identities tan^2-And also very frustrating when you can't figure them out It can be tricky because there's no precise waTrigonometricidentityprovingcalculator prove \tan^2(x)\sin^2(x)=\tan^2(x)\sin^2(x) en



Cofunction Identities In Trigonometry With Proof And Examples Owlcation
Example Using a trigonometric identity to solve a trig equation sin cos 1x x− = , within 0 2≤ Simplify tan^2 x sec^2 Ans 1 Use trig identity 1 tan^2 x = sec^2 x tan^2 x sec^2 x = 11 tan2 t= sec2 t use (twice
Start over and try something else tan4 t tan2 t = (tan2 t)(tan2 t 1)factor tan2 x = (sec2 t 1)(sec2 t);Students are taught about trig identities or trigonometric identities in school and are an important part of higherlevel mathematics So to help you understand and learn all trig identities we have explained here all the concepts of trigonometryAs a student, you would find the trig identity sheet we have provided here useful So you can download and print the identities PDFPrecalculus Proving Trigonometric Identities Example Prove the identity tan4 t tan2 t= sec4 t sec2 t tan4 t tan2 t = sint cost 4 sint cost 2 convert to sines and cosines = sint cost 4 sint cost 2 Yuck!
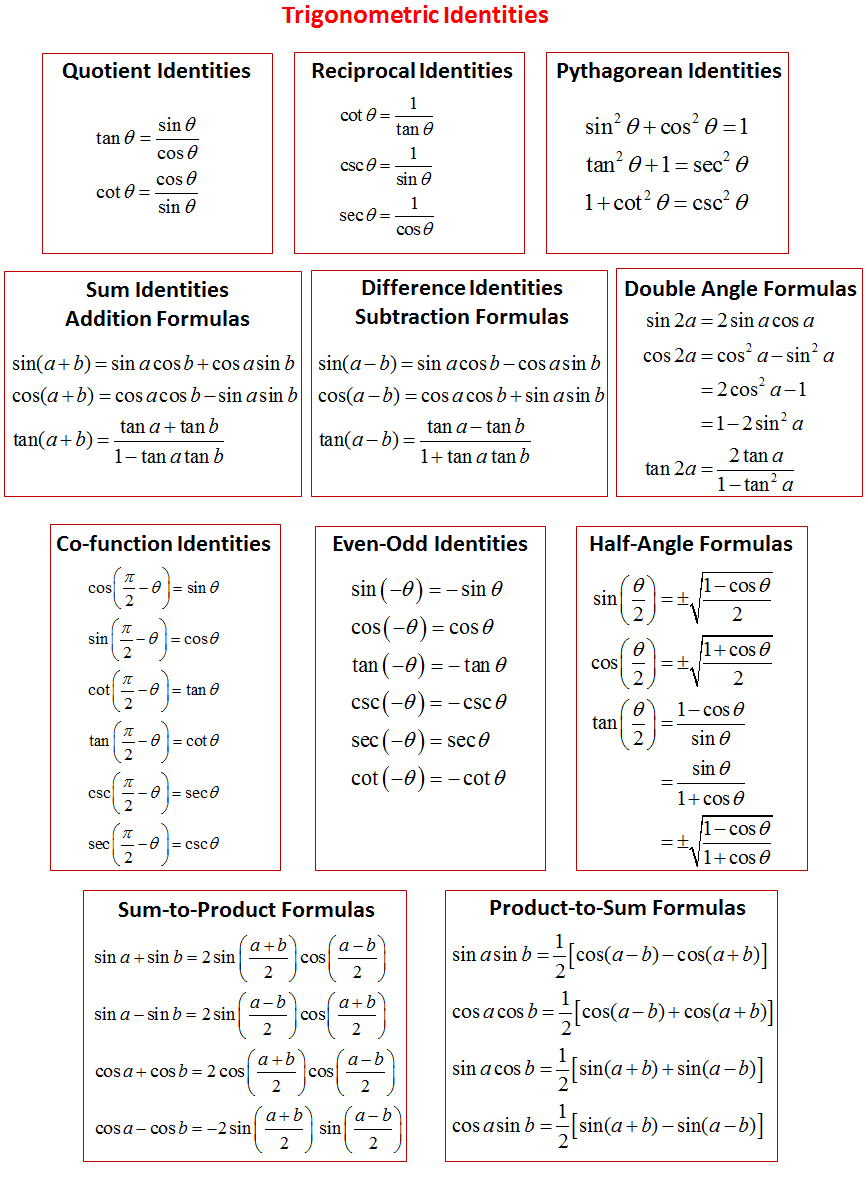
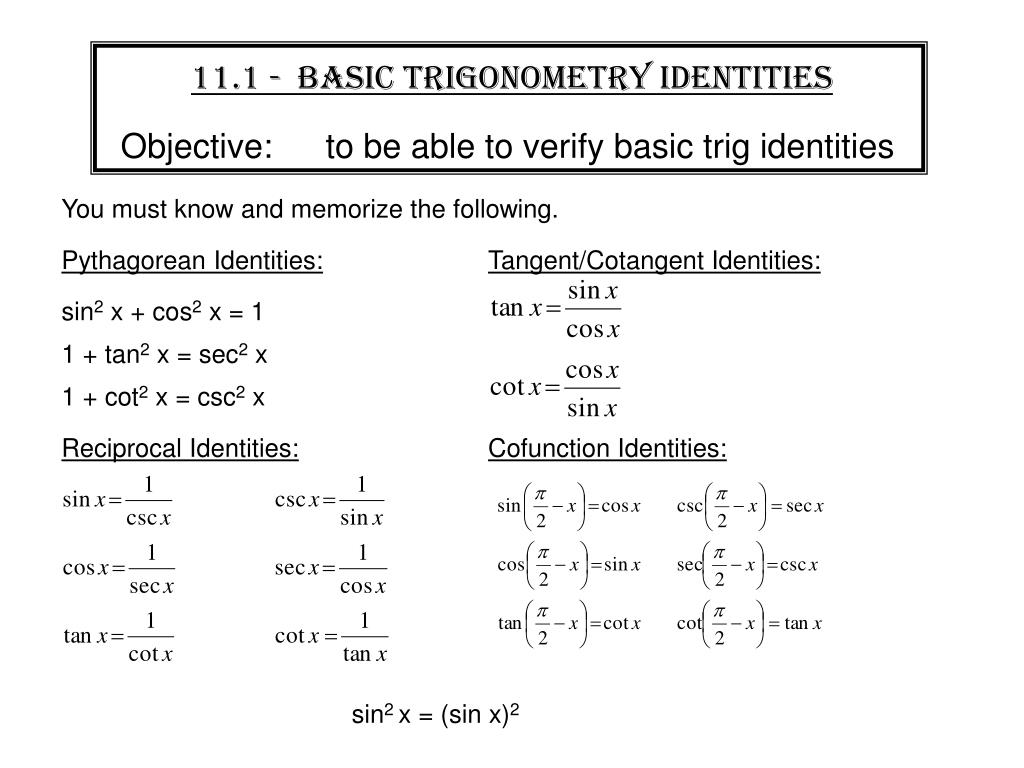
$$tan(2θ)={2 tan(θ)}/{1– tan^2(θ)}$$ Additional Trig Identities These three categories of trig identities are used less often You should look through them to make sure you understand them, but they typically don't need to be memorized HalfAngle Identities These are inversions of the doubleangle identities $$sin2(θ) = {1/2}(1cos (2θ))$$The half‐angle identity for tangent can be written in three different forms In the first form, the sign is determined by the quadrant in which the angle α/2 is located Example 5 Verify the identity Example 6 Verify the identity tan (α/2) = (1 − cos α)/sin α Example 7 Verify the identity tan (α − 2) = sin π/(1 cos α)The key Pythagorean Trigonometric identity are sin2(t) cos2(t) = 1 tan2(t) 1 = sec2(t) 1 cot2(t) = csc2(t)




Trig Identities Study Sheet




Trig Identities Sine Trigonometric Functions
The next set of fundamental identities is the set of reciprocal identities, which, as their name implies, relate trigonometric functions that are reciprocals of each other See Table 3 Recall that we first encountered these identities when defining trigonometric functions from right angles in Right Angle Trigonometry Here we will prove the problems on trigonometric identities As you know that the identity consists of two sides in equation, named Left Hand Side (abbreviated as LHS) and Right Hand Side (abbreviated as RHS)To prove the identity, sometimes we need to apply more fundamental identities, eg $\sin^2 x \cos^2 x = 1$ and use logical steps in order to lead oneMath Cheat Sheet for Trigonometry This website uses cookies to ensure you get the best experience



Www Nhvweb Net Vhs Math Jfranz Files 17 08 5 1 2 16 Even Solutions Pdf




Sci Pi Prove That 2 Tan45 A 1 Tan 45 A Cos2a Facebook
The table below summarizes the derivatives of \(6\) basic trigonometric functions In the examples below, find the derivative of the given function Solved Problems Click or tap a problem to see the solution The numerator can be simplified using the trigonometric identity \{1 {\tan^2}x = {\sec ^2}x } = {\frac{1}{{{{\cos }^2}xTrigonometric Identities prove tan^2 (x)sin^2 (x)=tan^2 (x)sin^2 (x)TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITIES By Joanna GuttLehr, Pinnacle Learning Lab, last updated 5/08 Pythagorean Identities sin (A) cos (A) 1 1 tan (A) sec (A) 1 cot (A) csc2 (A)Quotient Identities sin( )




Lesson 5 2 Verifying Trigonometric Identities Trig Ridge Style



Http Www Humbleisd Net Cms Lib2 Tx Centricity Domain 2966 Chapter 9 1 9 4 notes key Pdf
Verifying trigonometric identities Process make one side look exactly like the other using a combination of trigonometric identities and algebra You can work with only one side at a time If all else fails, turn everything into sine x and cosine x and see what happens!Trig Cheat Sheet Definition of the Trig Functions Right triangle definition For this definition we assume that 0 2 p1cot 2 θ = cosec 2 θ




Trigonometric Identities Trigonometric Functions Trigonometry
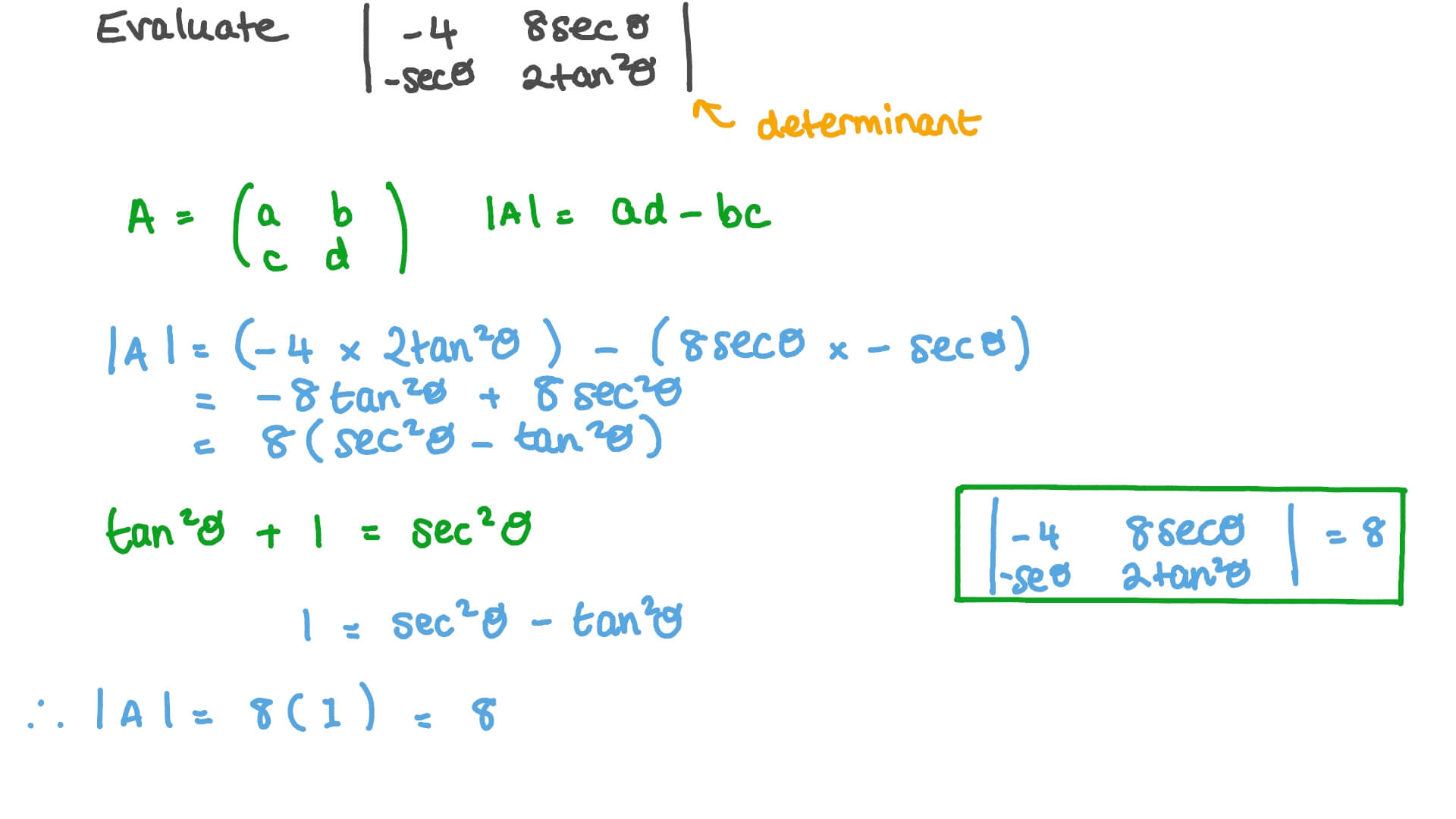



Question Video Determinants Of Matrices Involving Trigonometric Functions Nagwa
Trigonometry The field emerged in the Hellenistic world during the 3rd century BC from applications of geometry to astronomical studies The Greeks focused on the calculation of chords, while mathematicians in India created the earliestknown tables of values for trigonometric ratios (also called trigonometric functions) such as sineA trigonometric identity in one variable is an equality that involves trigonometric functions and is true for all values of the variable for which both sides of the equality are defined Recall the Pythagorean theorem that relates the lengths of the sides of a right triangle \{a^2} {b^2} = {c^2},\ where \(a,b\) are the lengths of the triangle's legs and \(c\) is the length of itsTrigonometric identities are equalities involving trigonometric functions An example of a trigonometric identity is sin 2 θ cos 2 θ = 1 \sin^2 \theta \cos^2 \theta = 1 sin2 θcos2 θ = 1 In order to prove trigonometric identities, we generally use other known identities such as Pythagorean identities



2
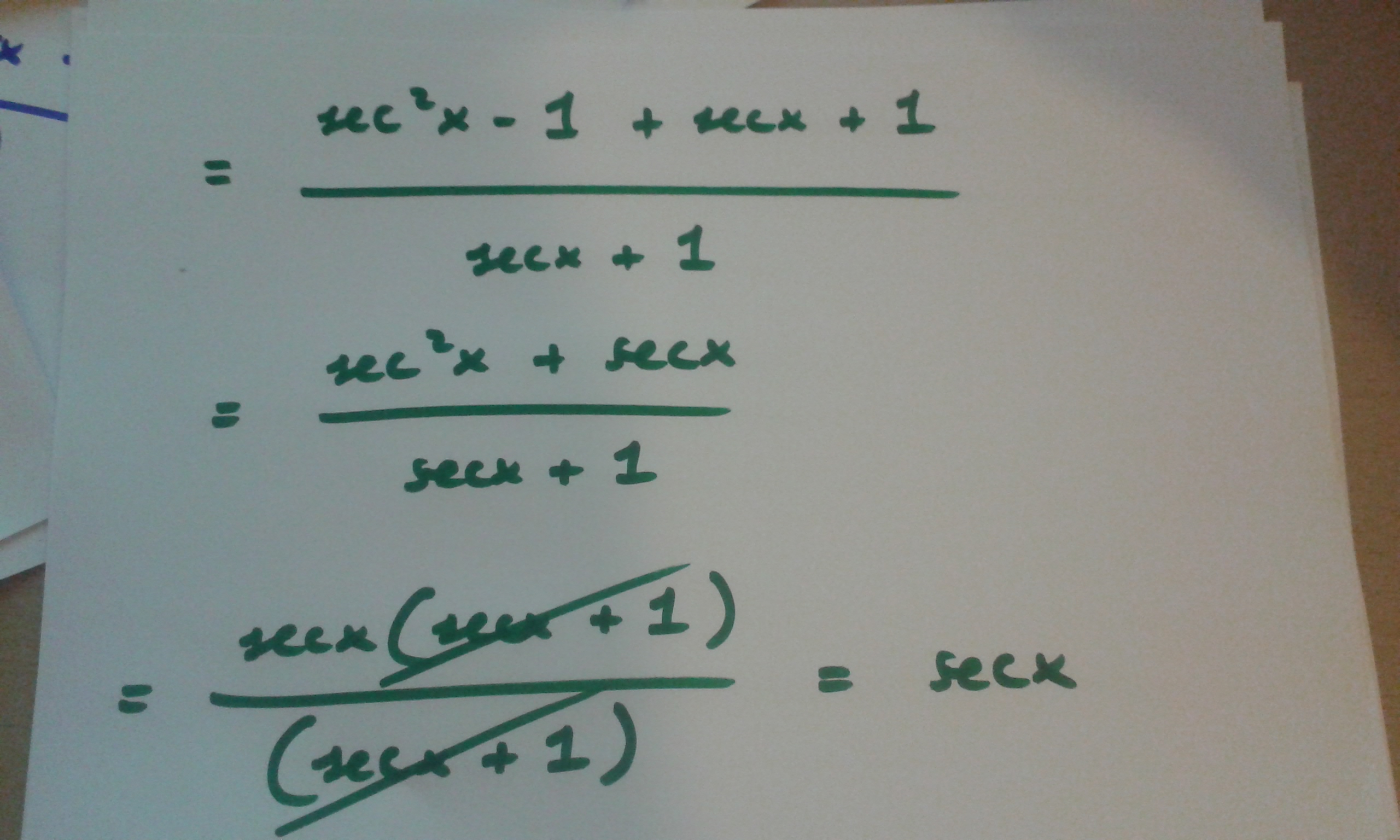



How Do You Prove Tan 2x Secx 1 1 Secx Socratic
Math2org Math Tables Trigonometric Identities sin (theta) = a / c csc (theta) = 1 / sin (theta) = c / a cos (theta) = b / c sec (theta) = 1 / cos (theta) = c / b tan (theta) = sin (theta) / cos (theta) = a / b cot (theta) = 1/ tan (theta) = b / a sin (x) = sin (x)Trigonometric Identities 43 Introduction A trigonometric identity is a relation between trigonometric expressions which is true for all values of the variables (usually angles) There are a very large number of such identities In this Section we discuss only the most important and widely used Any engineer using trigonometry in an applicationTrigonometric Identities The Six Trigonometric Functions Reciprocal Identities ℎ 1 sin = ℎ = csc = = cos = ℎ = sec = ℎ = tan = = cot = = 1 sin = csc csc = sin 1 tan 2 = 1cos sin Co Function Identities sin 0 $1,=cos csc 0 $1,=sec cos 0 $1,=sin sec



Solved Find The Remaining Five Trigonometric Functions Of 0 See Example 1 Sin A 0 In Quadrant Ii 32 Cos 0 0 In Quadrant I 33 Tan 0 Course Hero




Pythagorean Identities Examples Practice Problems Trigonometry Youtube
Periodicity of trig functions Sine, cosine, secant, and cosecant have period 2 π while tangent and cotangent have period π Identities for negative angles Sine, tangent, cotangent, and cosecant are odd functions while cosine and secant are even functions Ptolemy's identities, the sum and difference formulas for sine and cosinePythagorean Trig Identities Pythagoras Trig Identities are the trigonometric identities which actually the true representation of the Pythagoras Theorem as trigonometric functions So, these identities help us to fundamentally decide the relationship between different sine, cosine, and tan trigonometric function62 Trigonometric identities (EMBHH) An identity is a mathematical statement that equates one quantity with another Trigonometric identities allow us to simplify a given expression so that it contains sine and cosine ratios only This enables us to solve equations and also to prove other identities




How Do You Prove Tan X 1 Tan X 1 1 Cot X 1 Cot X Socratic



Algebra Ii Sem2 Activity 2 5 1 Trig Identities Gauthmath
Verifying Trigonometric Identities Identities enable us to simplify complicated expressions They are the basic tools of trigonometry used in solving trigonometric equations, just as factoring, finding common denominators, and using special formulas are the basic tools of solving algebraic equationsTan is an "odd" identity quotient identity (for tangent) algebra/ simplify 1) 2) cos tan (x) Strategy 1) get rid of the negatives 2) üy to change terms to sin's and COS's 3) simplFy • tan (x) tan x sm x cos x smx cos (x) cosx • cosx • Prove Strategy$\tan^2{\theta} \,=\, \sec^2{\theta}1$ The square of tan function equals to the subtraction of one from the square of secant function is called the tan squared formula It is also called as the square of tan function identity Introduction The tangent functions are often involved in trigonometric expressions and equations in square form The expressions or equations can be possibly simplified by transforming the tan




Sample Problems Cos 2 X Tan2 X Tan 2 Csc 2 Tan Sec X Tan X Cos X Sin 4 X Cos 4 X 1 2 Cos 2 X Pdf Free Download



Www Interborosd Org Site Handlers Filedownload Ashx Moduleinstanceid 62 Dataid Filename Trig Identity Secret Message Ws page 1 Pdf
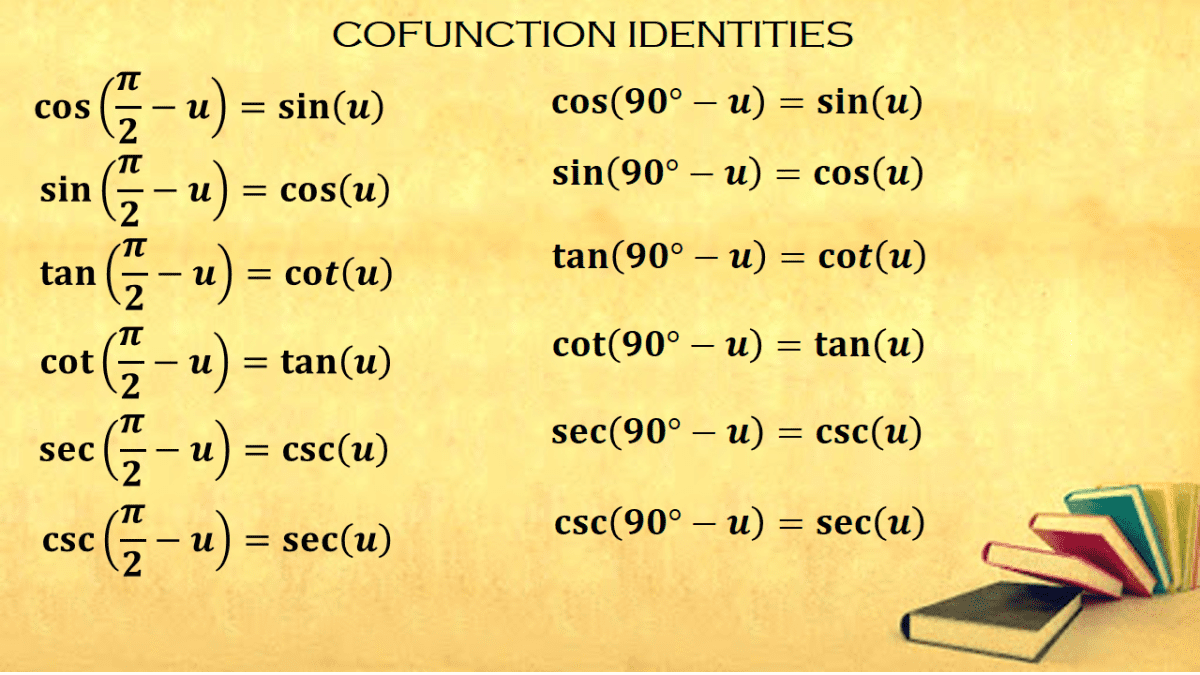
Identities expressing trig functions in terms of their complements cos t = sin( /2 – t ) sin t = cos( /2 – t ) cot t = tan( /2 – t ) tan t = cot( /2 – t )Trigonometricidentitycalculator Prove tan^{2} x * sin^{2} x = tan^{2} x sin^{2} x enNow, using the trigonometric identity 1tan 2 a = sec 2 a sec 2 A = 1 (3/4) 2 sec 2 A = 25/16 sec A = ±5/4 Since, the ratio of lengths is positive, we can neglect sec A = 5/4 Therefore, sec A = 5/4 Example 2 (1 – sin A)/(1 sin A) = (sec A – tan A) 2 Solution Let us take the Left hand side of the equation LHS = (1 – sin A)/(1 sin A)




How To Solve Trigonometric Equations 8 Steps With Pictures



Trigonometric Identities Sin 2 X Cos 2 X Tan 2 X Youtube
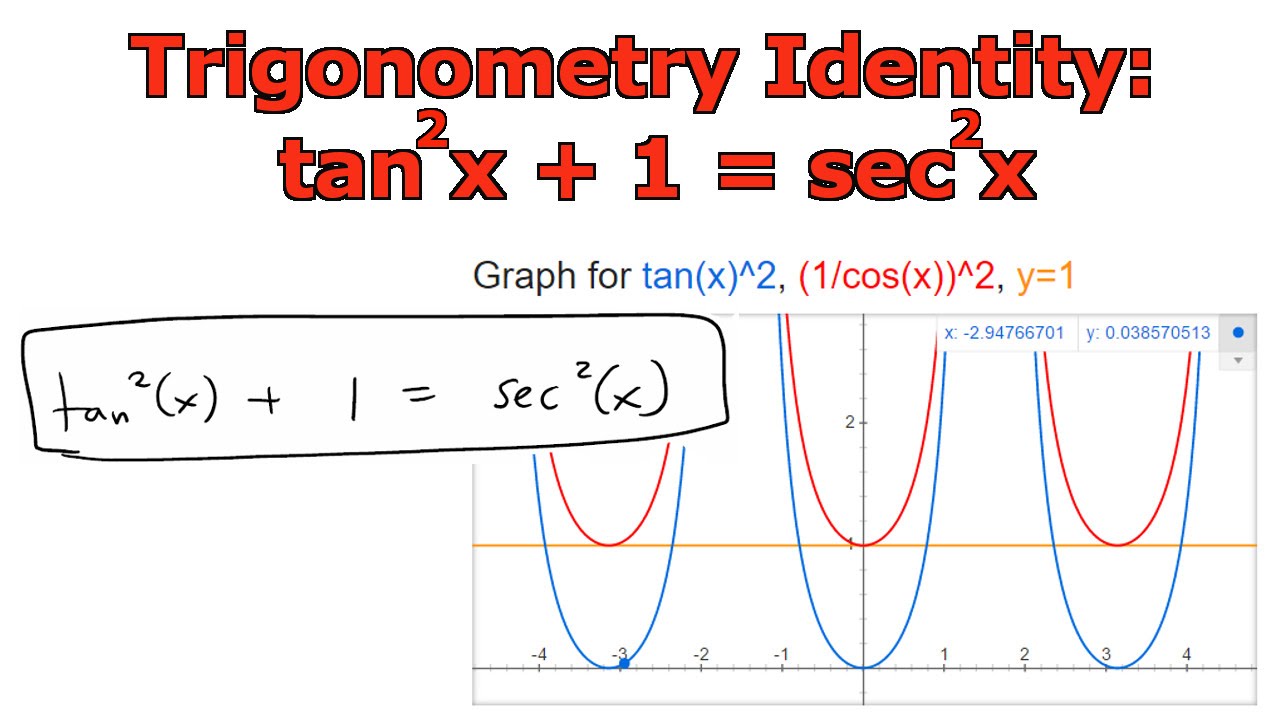
This is one of the Pythagorean identities In the same way, we can derive two other Pythagorean trigonometric identities 1tan 2 θ = sec 2 θ; Some trigonometric identities follow immediately from this de nition, in particular, since the unit circle is all the points in plane with xand ycoordinates satisfying x2 y2 = 1, we have cos2 sin2 = 1 Other trignometric identities re ect a much less obvious property of the cosine and sine functions, their behavior under addition of angles Middle School answer answered PLEASE Using the following tan(x) = sin(x)/cos(x) cos^2(x)sin^2(x) = 1 sec(x) = 1/cos(x) for cos(x)!=0, we have 1tan^2(x) = cos^2(x)/cos^2(x) (sin(x)/cos(x))^2 =cos^2(x)/cos^2(x)sin^2(x)/cos^2(x) =(cos^2(x)sin^2(x))/cos^2(x) =1/cos^2(x)



Http Gato Docs Its Txstate Edu Jcr 9ff 4037 48ff 1f A3486fb Trigonometric identities Pdf



Trigonometric Identities Solutions Examples Videos
Trigonometry Identities Examples and Strategies cosine is an "even" identity;Trig Equations and Identities wwwnaikermathscom 4 (a) Given that sin q = 5 cos q, find the value of tan q (1) (b) Hence, or otherwise, find the values of q in the interval 0 £ q < 360° for which sin q = 5 cos q, giving your answers to 1 decimal place (3) June 06 Q6 5 (a) Show that the equation 3 sin2 q – 2 cos2 q = 1 can be written asTrigonometry Identities Quotient Identities tan𝜃=sin𝜃 cos𝜃 cot𝜃=cos𝜃 sin𝜃 Reciprocal Identities csc𝜃= 1 sin𝜃 sec𝜃= 1 cos𝜃 cot𝜃= 1 tan𝜃 Pythagorean Identities sin2𝜃cos2𝜃=1 tan 2𝜃1=sec2𝜃 1cot2𝜃=csc2𝜃 Sum & Difference Identities sin( )=sin cos cos sin



Trigonometric Identity Examples Solutions Videos



2
Verifying trigonometric identities can be super fun!View trig identities worksheetpdf from CALCULUS 1P05 at Brock University Trigonometric Identities 1 Lecture Notes page 1 Sample Problems Prove each of the following identities



Trig Identities Crossword Wordmint



Http Www Mrsfruge Com Uploads 1 2 0 0 Precalculus Chapter 5 Packet Answers Pdf



Trigonometry Reciprocal Identities Expii



Www Brockport Edu Academics Tutoring Docs Trigonometric Identities Pdf



Www2 Math Binghamton Edu Lib Exe Fetch Php People Mckenzie Trig Identities Worksheet With Answers 2 Pdf




Trig Identities Studying Math Math Methods Homeschool Math



Ppt Warm Up Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Www Basd K12 Wi Us Faculty Mbuteyn Trig identities ws Ch 9 key Pdf




Trigonometric Identity Examples Solutions Videos



1
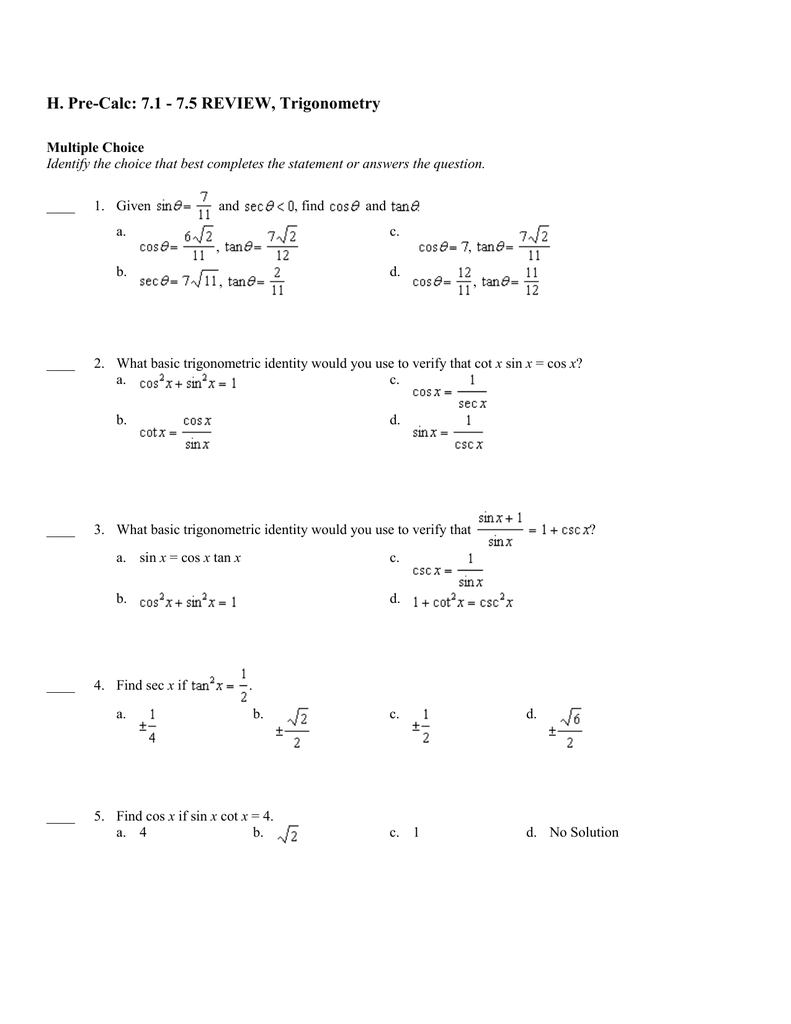



H Pre Calc 7 1 7 5 Review Trigonometry




Chapter 8 Trigonometric Identities Pdf Trigonometric Functions Differential Geometry
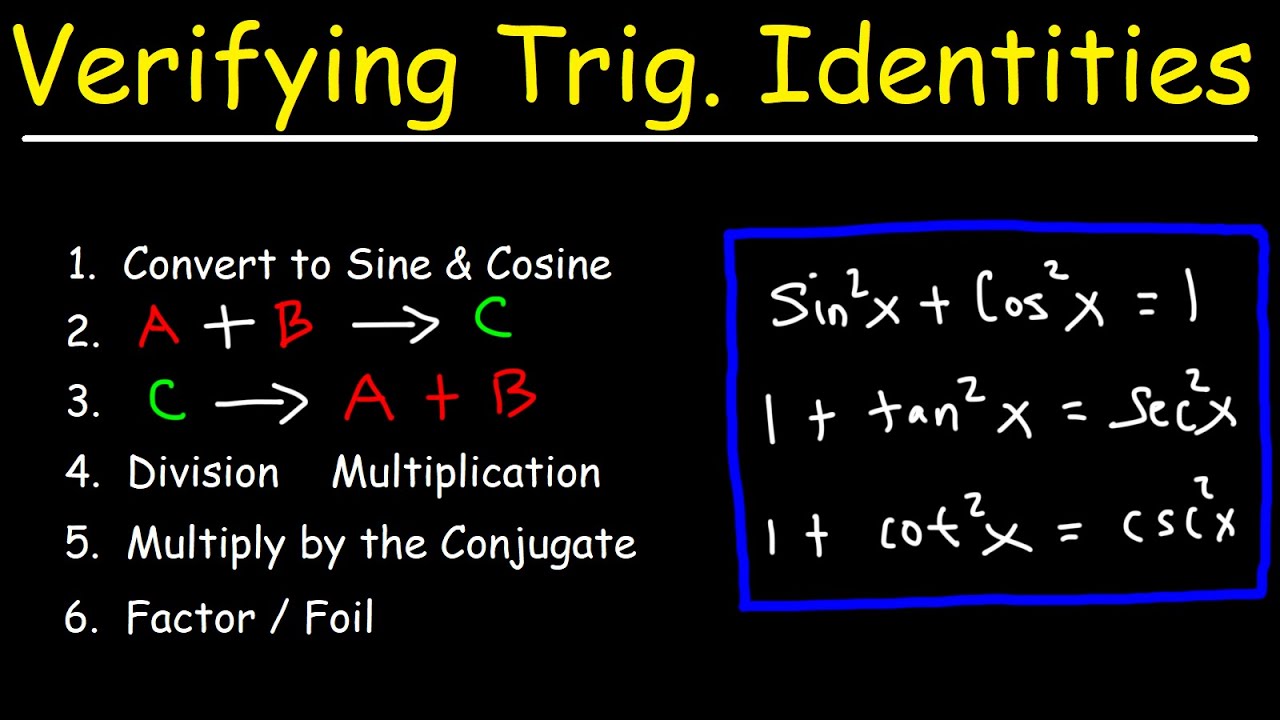



Verifying Trigonometric Identities Youtube



Www Alamo Edu Siteassets Nvc Academics Programs Math Documents 12 Trigonometric Identities Pdf



Www Carlisleschools Org Common Pages Userfile Aspx Fileid
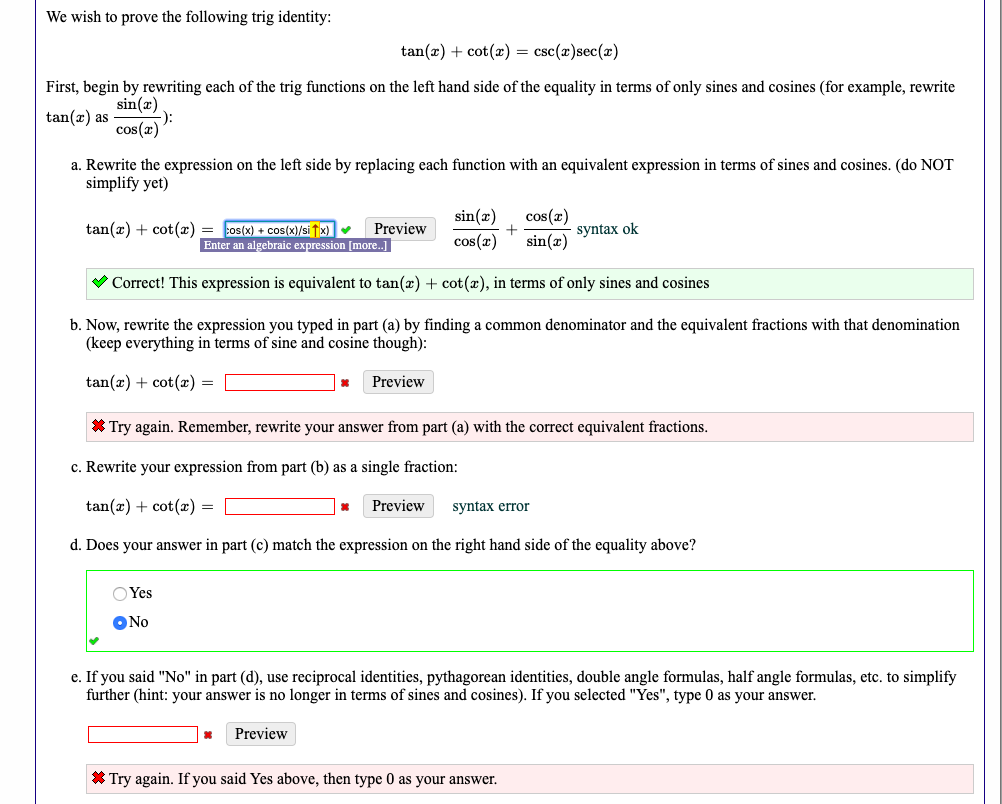



We Wish To Prove The Following Trig Identity Tan X Chegg Com



Www2 Math Binghamton Edu Lib Exe Fetch Php People Mckenzie Trig Identities Worksheet With Answers 2 Pdf



Trig Identities All List Of Trigonometric Identities Learn Trigonometry



Lsamathwilson Weebly Com Uploads 2 2 5 4 Pc 5 2 Verifying Trigonometric Identities Solutions Pdf



Web Stanford Edu Class Archive Math Math Math 1144 Files Trig Pdf
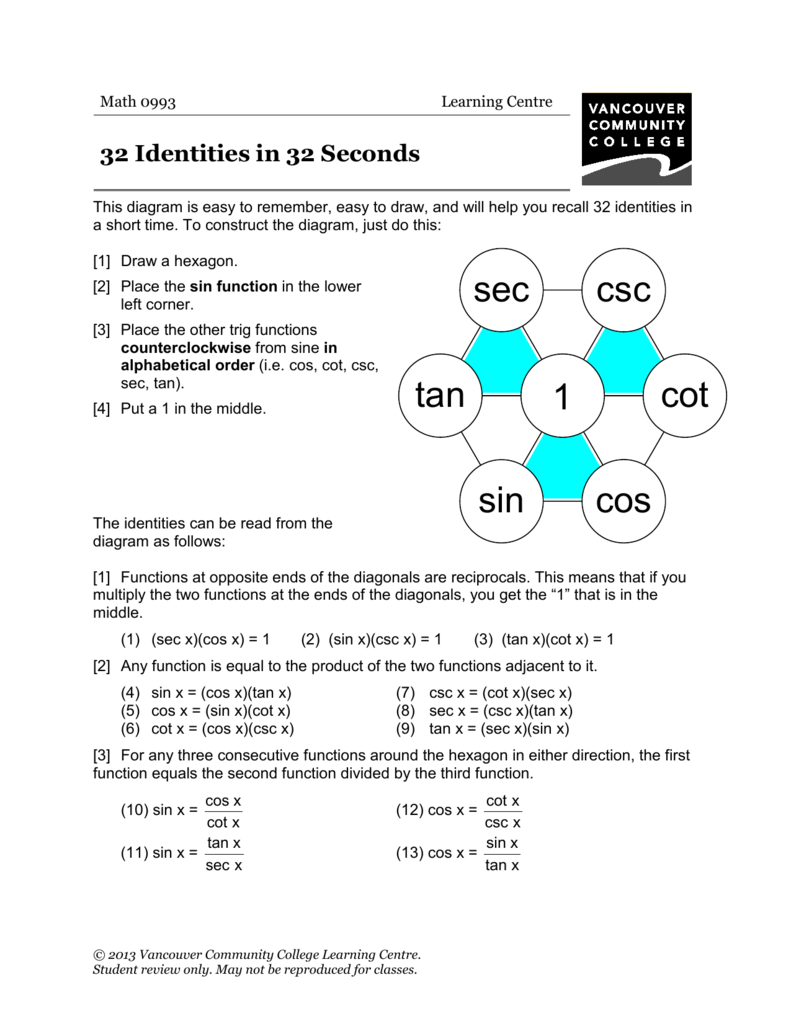



32 Trig Identities
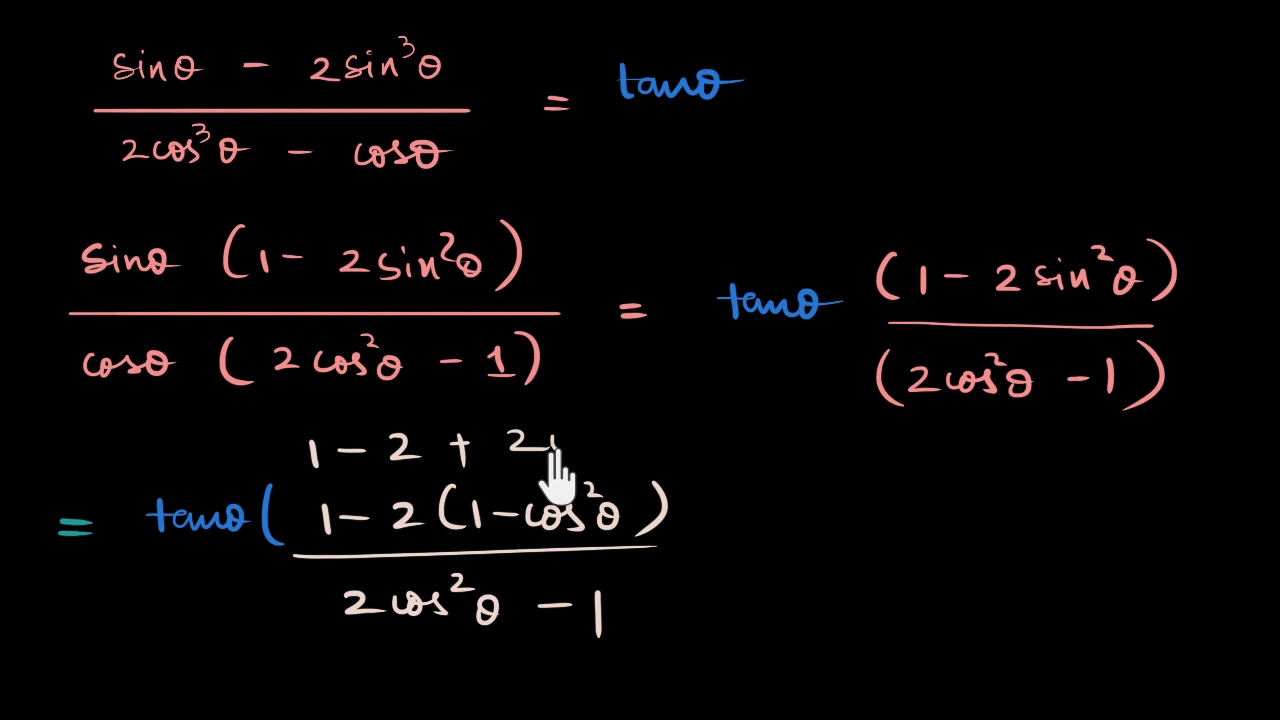



Trigonometric Identity Example Proof Involving Sin Cos And Tan Video Khan Academy




Higher Secondary School Trigonometry Problem Mathematics Stack Exchange



Www Whiteplainspublicschools Org Cms Lib Ny Centricity Domain 360 th identities packet 16 Pdf




7 2 Verifying Trigonometric Identities Ppt Download




7 2 Verifying Trigonometric Identities Ppt Download



Schoolwires Henry K12 Ga Us Cms Lib Ga Centricity Domain 1610 Unit 4 test trig identities a Pdf
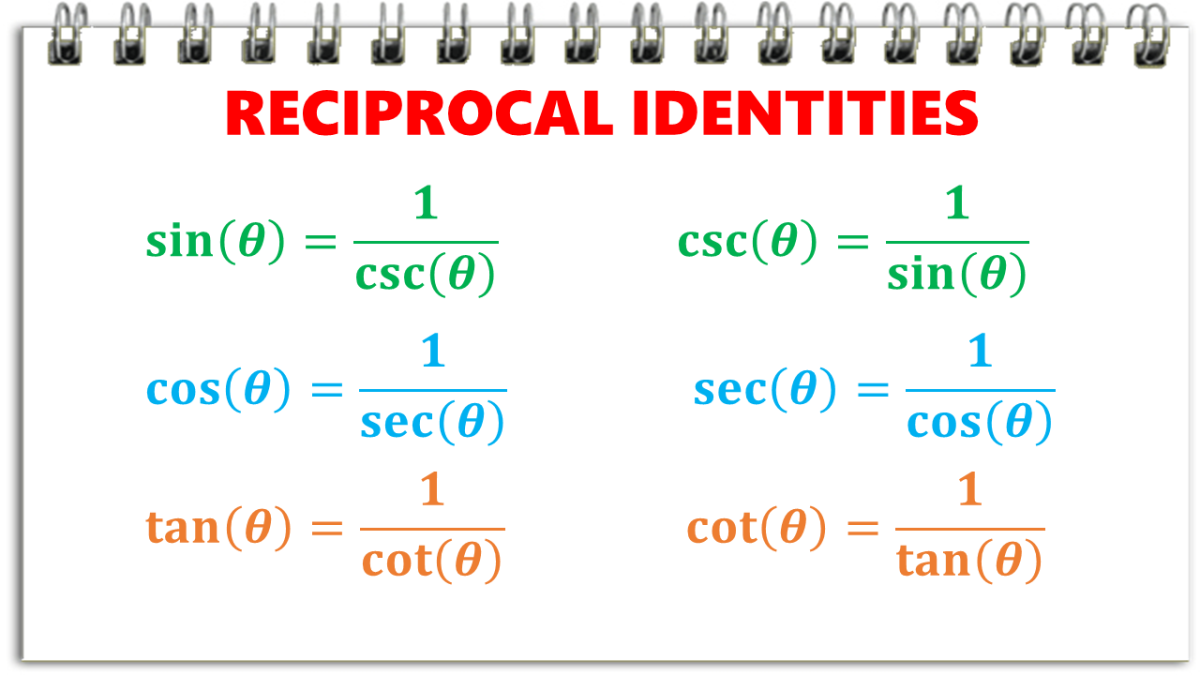



Reciprocal Identities In Trigonometry With Examples Owlcation



Solved Prove The Following Trig Identity Sec 2 X 2secx Cosx Cos 2 X Tan 2 X Sin 2 X Course Hero



1




Cos Sin Tan Csc Sec Cot



Trigonometric Identity Example Proof Involving All The Six Ratios Video Khan Academy



Trigonometry Identity Tan 2 X 1 Sec 2 X Youtube



Http College Cengage Com Mathematics Larson Trigonometry 6e Instructors Downloads Instr Trig6 S21 Pdf




Trigonometric Identities




List Of Trigonometric Identities 2 Docx Document



Chapter 5 Trigonometric Identities Review Sheet




Quiz Worksheet Trigonometric Identities Unit Circles Study Com




Sample Problems Cos 2 X Tan2 X Tan 2 Csc 2 Tan Sec X Tan X Cos X Sin 4 X Cos 4 X 1 2 Cos 2 X Pdf Free Download




10 4 Evaluate Each Of The Following Definite Chegg Com




Cofunction Identities In Trigonometry With Proof And Examples Owlcation




Trigonometric Identities




List Of Trigonometric Identities Wikipedia
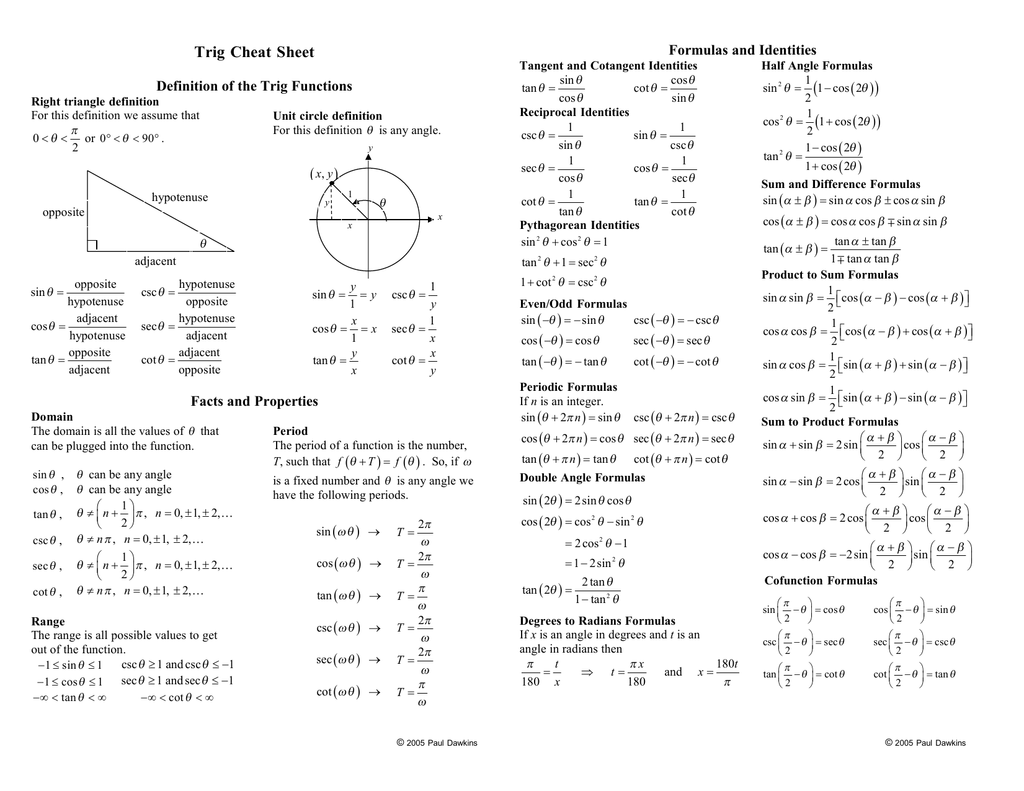



Trig Identities Table Of Trigonometric Identities
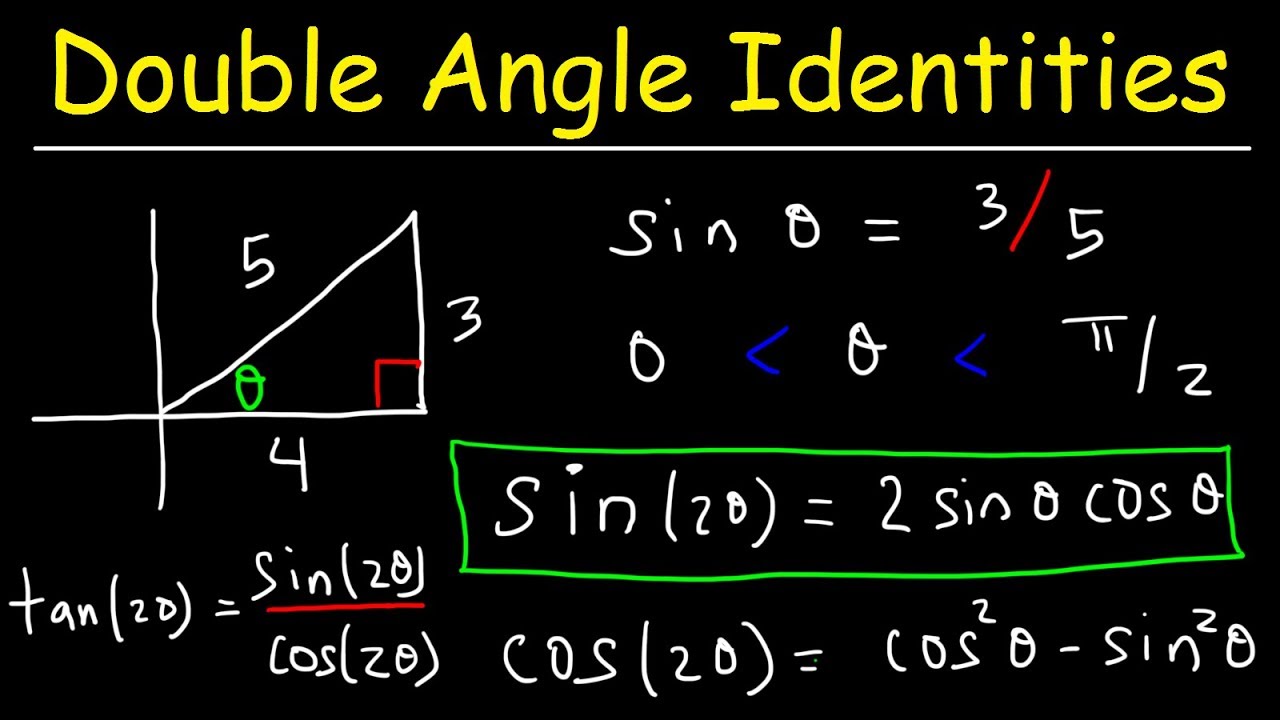



Double Angle Identities Formulas Of Sin Cos Tan Trigonometry Youtube



Www2 Math Binghamton Edu Lib Exe Fetch Php People Mckenzie Trig Identities Worksheet With Answers 2 Pdf




Double Angle Identities Joke Worksheet Math Love




Sample Problems Cos 2 X Tan2 X Tan 2 Csc 2 Tan Sec X Tan X Cos X Sin 4 X Cos 4 X 1 2 Cos 2 X Pdf Free Download
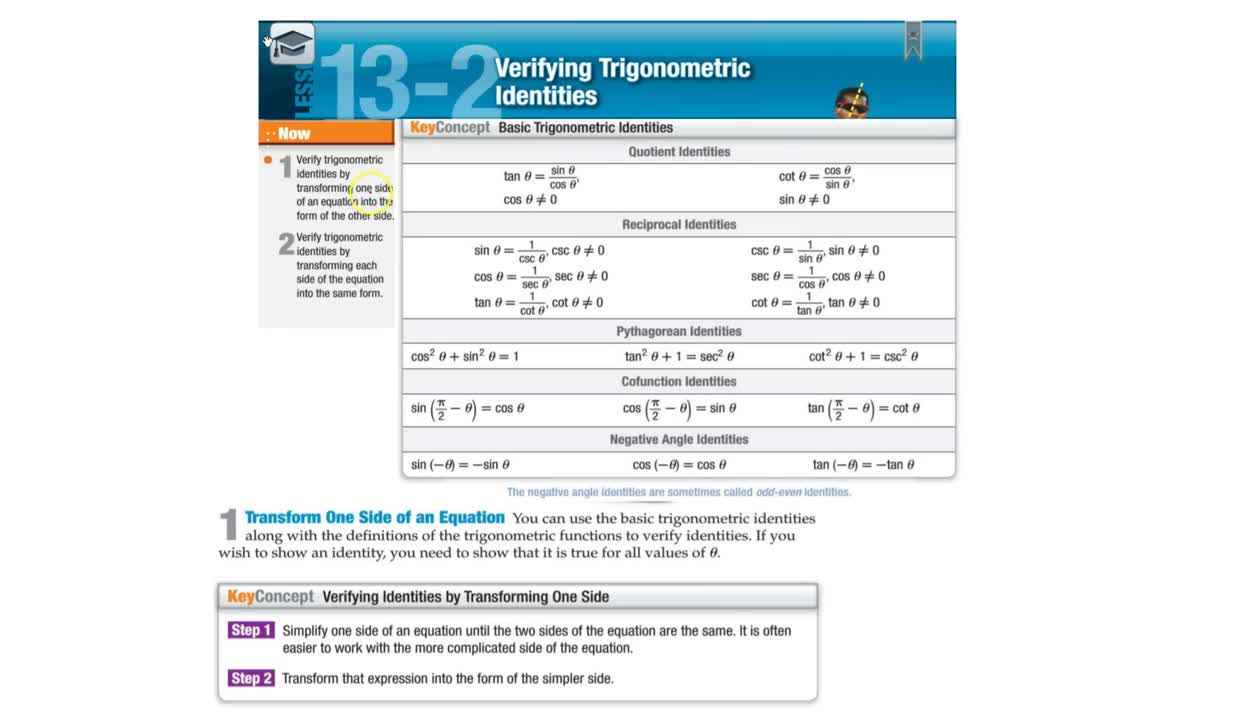



Honors Algebra 2 Trig Notes Chapter 13 Section 2 Bishop Amat Memorial High School




Cos Sin Tan Csc Sec Cot



1
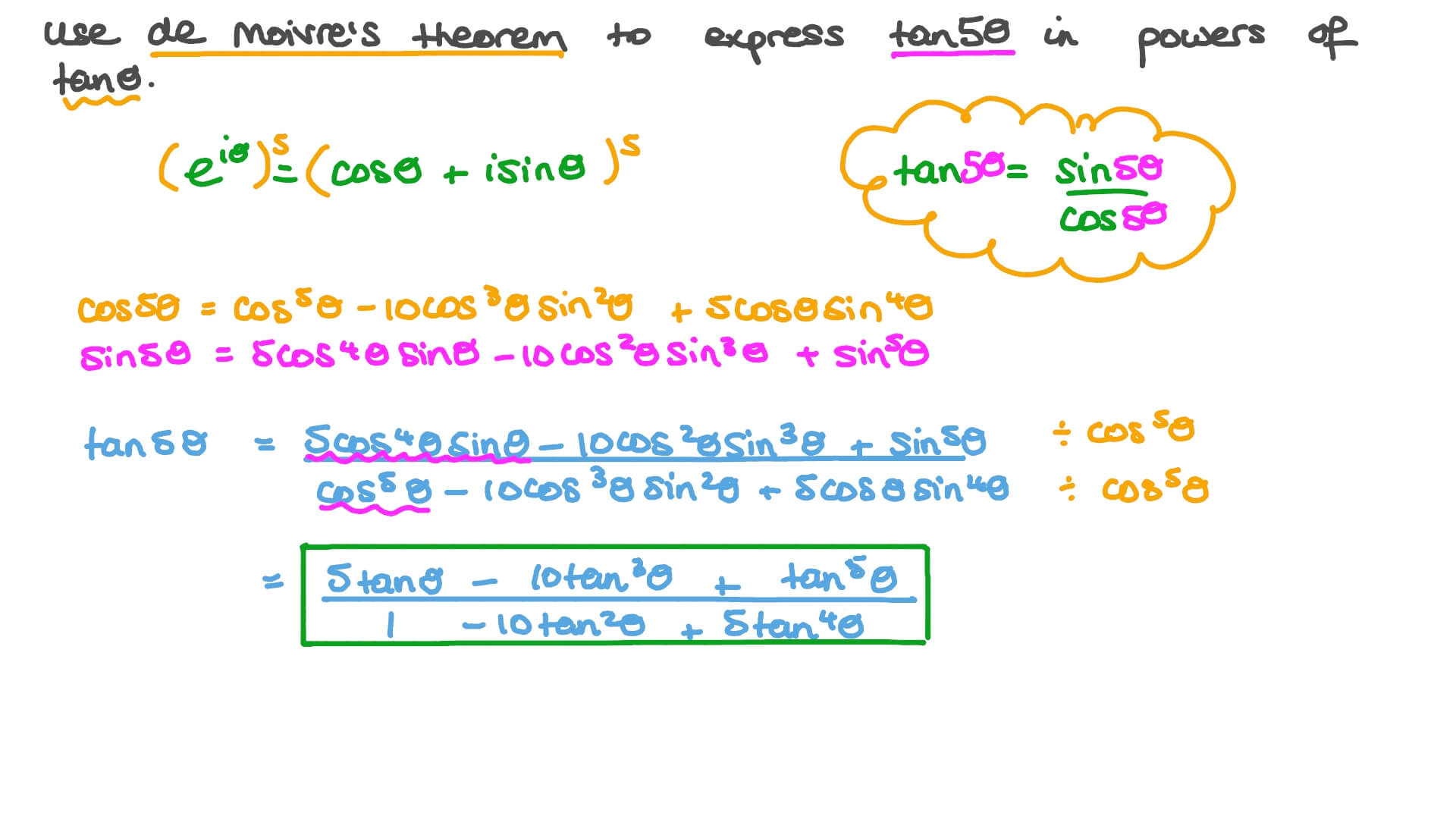



Question Video Using De Moivre S Theorem To Derive Trigonometric Identities Nagwa
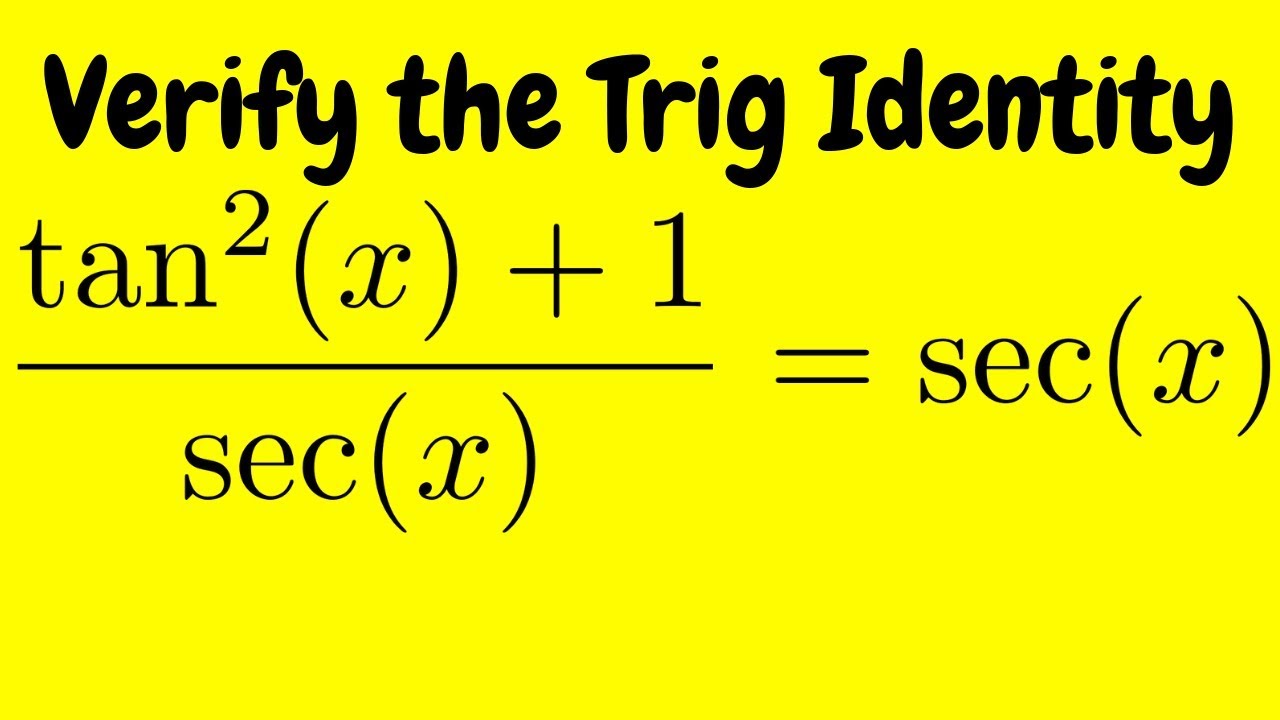



Verifying A Trigonometric Identity Tan 2 X 1 Sec X Sec X Youtube



Http Www Whsd K12 Pa Us Userfiles 1598 Classes 9713 Trig chapter 5 notes Pdf



Http Www Northallegheny Org Cms Lib9 Pa Centricity Domain 1308 7 1 day 1 notes Pdf



Http Www Highlandhhs Ss6 Sharpschool Com Userfiles Servers Server File High school Jph Precalculus solutions Unit 2 solutions Pdf
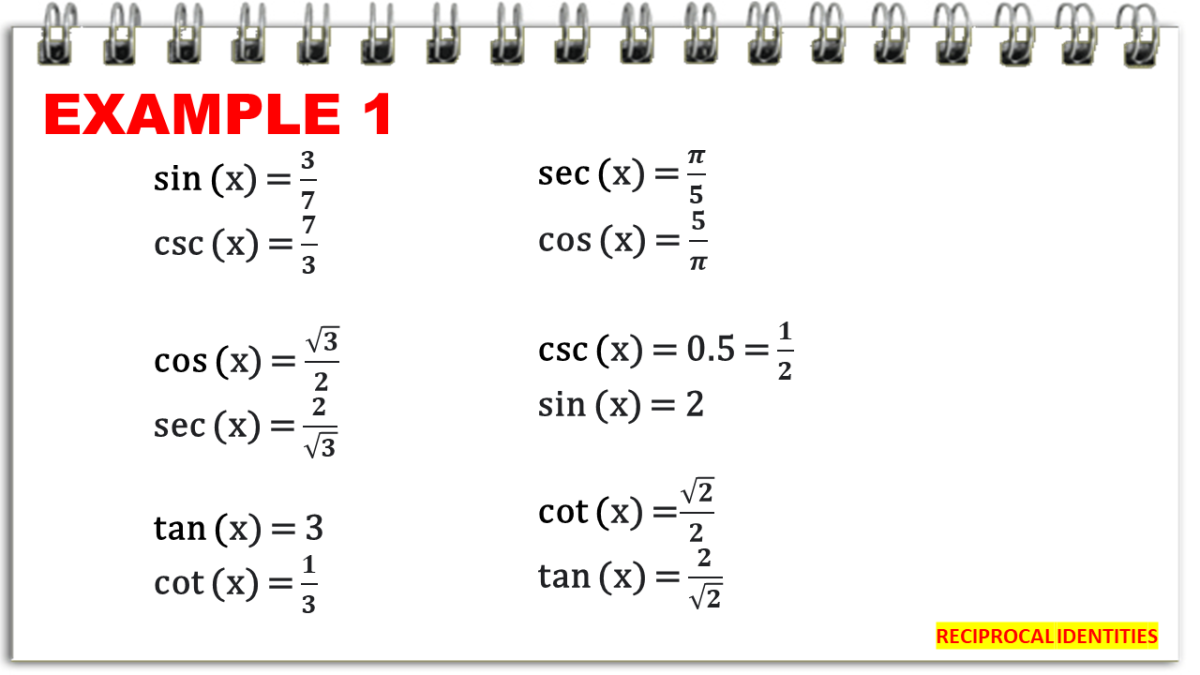



Reciprocal Identities In Trigonometry With Examples Owlcation
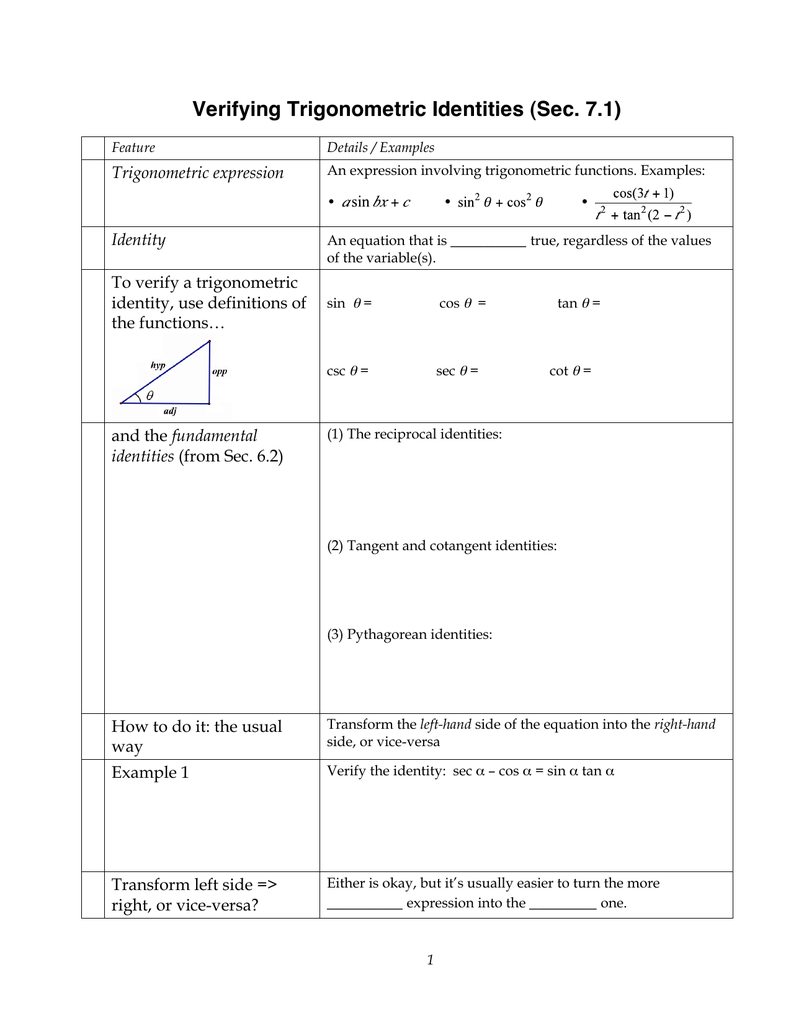



Verifying Trigonometric Identities Sec 7 1 Trigonometric Expression Identity




How Do You Prove The Identities Cosx Secx Sinx Cscx Sec 2x Tan 2x Socratic



Mi Schoolwires Net Cms Lib Mi Centricity Domain 433 Trig identities notes and hw packet march 18 Pdf



Wou Edu Mathcenter Files 15 09 Trig Identities Pdf
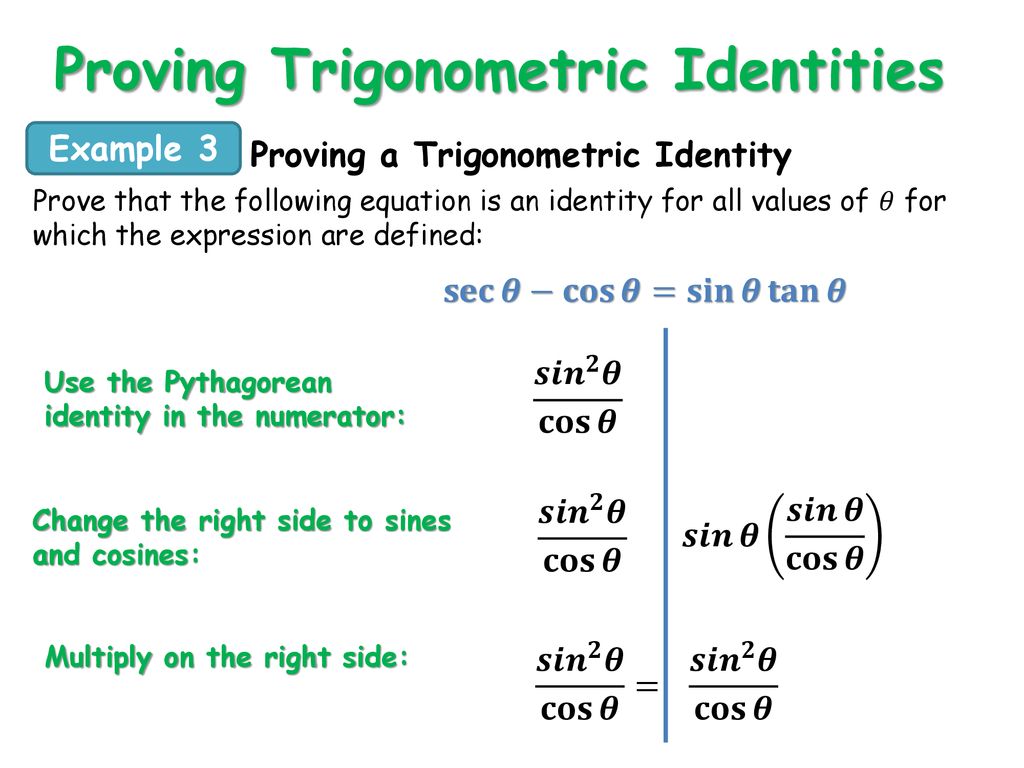



Trigonometry Identities And Equations Ppt Download
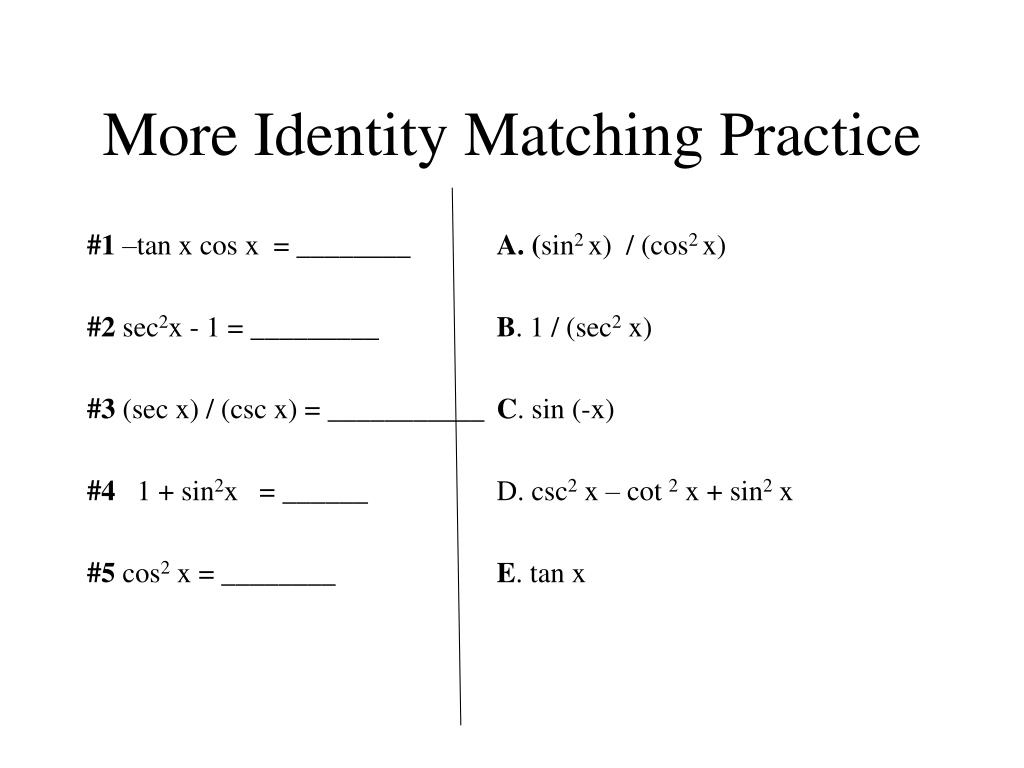



Ppt 5 1 Fundamental Trig Identities Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
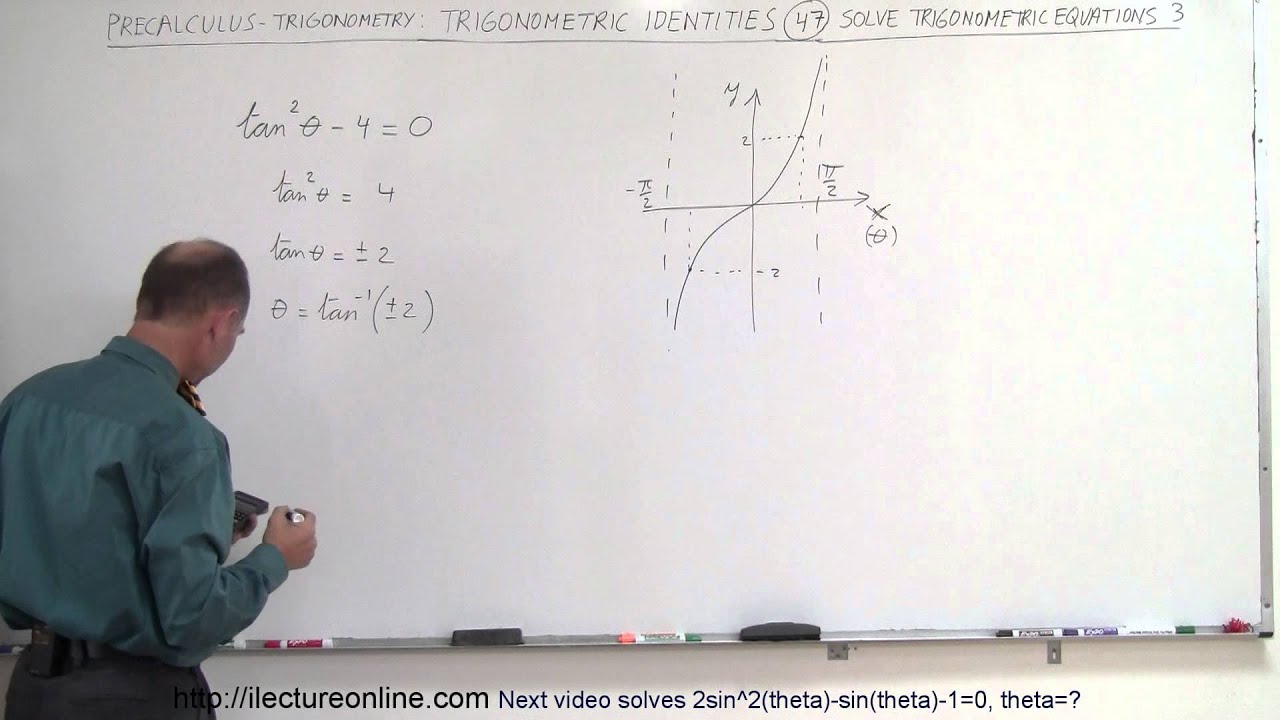



Precalculus Trigonometry Trig Identities 47 Of 57 Solve Tan 2 Theta 4 0 Theta Youtube
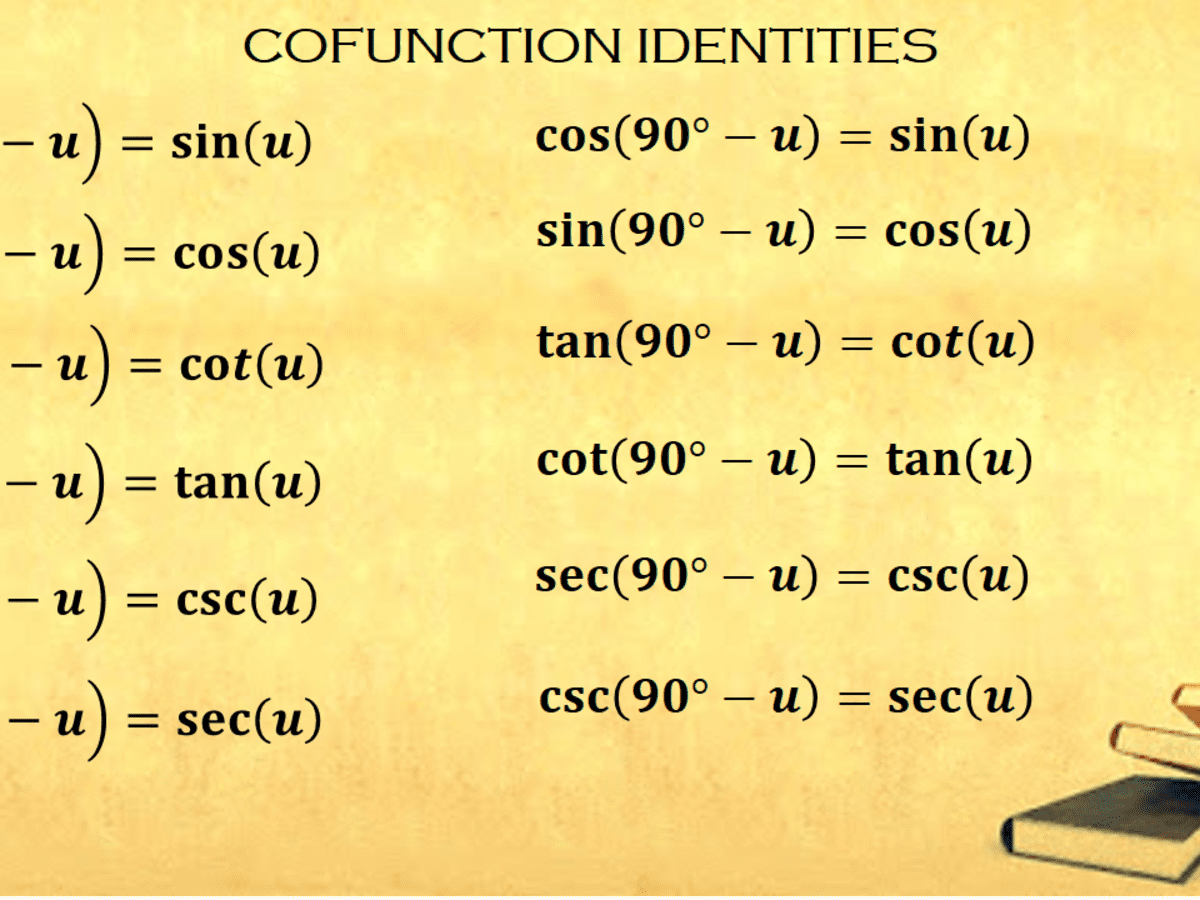



Cofunction Identities In Trigonometry With Proof And Examples Owlcation




Powers Of Trigonometric Functions
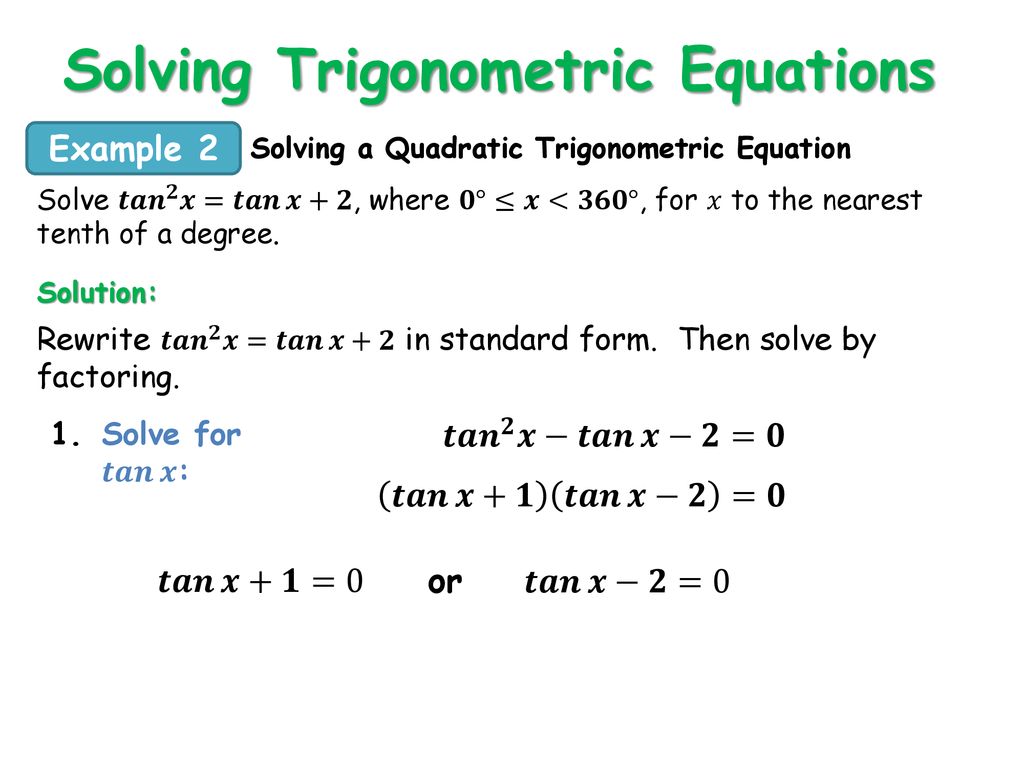



Trigonometry Identities And Equations Ppt Download



Www Csd49 Org Userfiles 91 Classes 3557 Unit 6 trigonometric identities equations notes review and study guide Pdf Id 7750
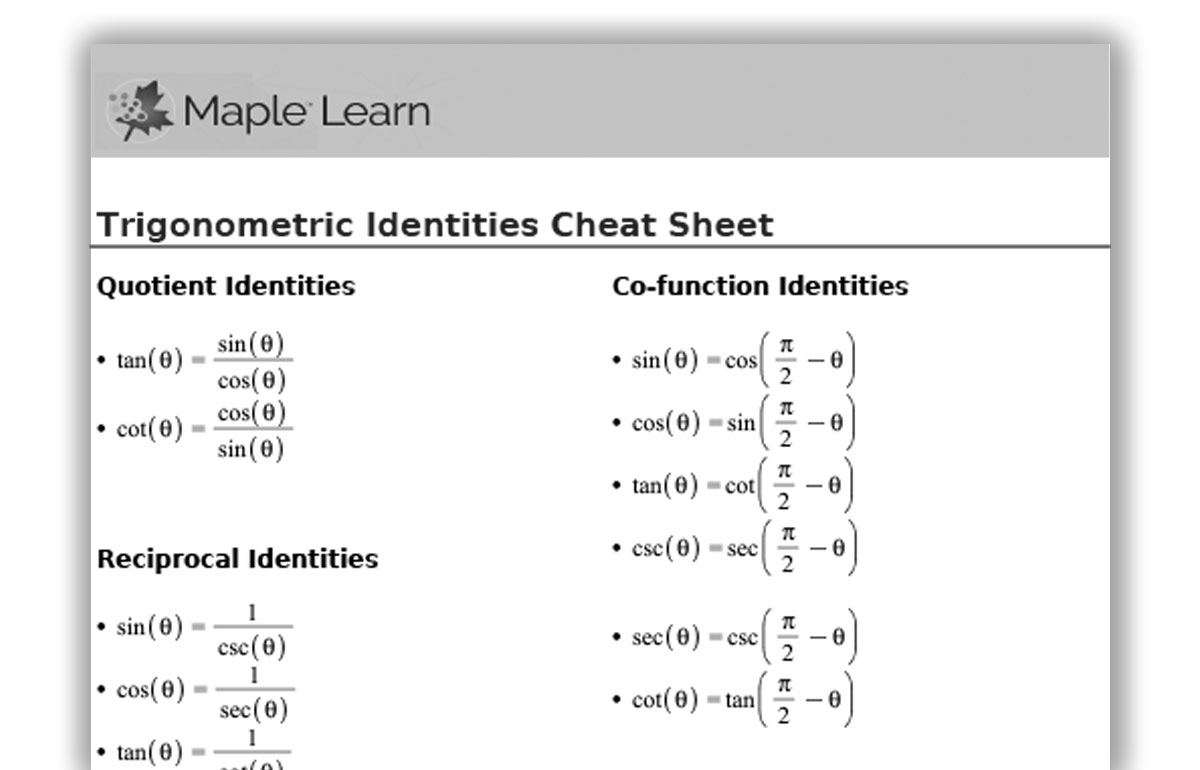



Trig Identities Maple Learn Maplesoft




Check My Work Evaluating Tan Frac 7 Pi 8 Using A Half Angle Formula Mathematics Stack Exchange




Microsoft Word A 3 1 Basic 8 Trig Identities Sine Trigonometric Functions




How Do You Simplify Sec 4x Tan 4x Sec 2x Tan 2x Socratic
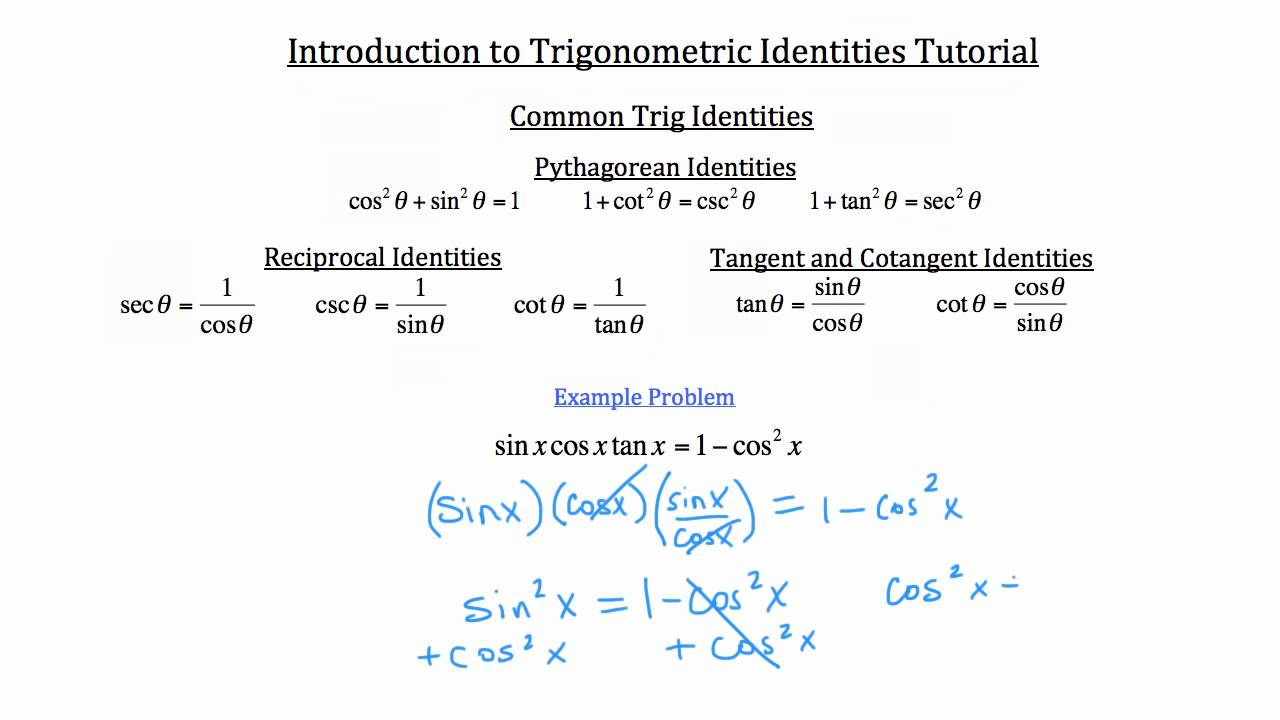



Trigonometric Identities A Plus Topper




Trigonometric Identities




Solved Inquiry 11 8 Marks Prove The Following Trig Iden Chegg Com



Www Jmap Org Worksheets F Tf C 8 Provingtrigonometricidentities Pdf




Cos Sin Tan Csc Sec Cot
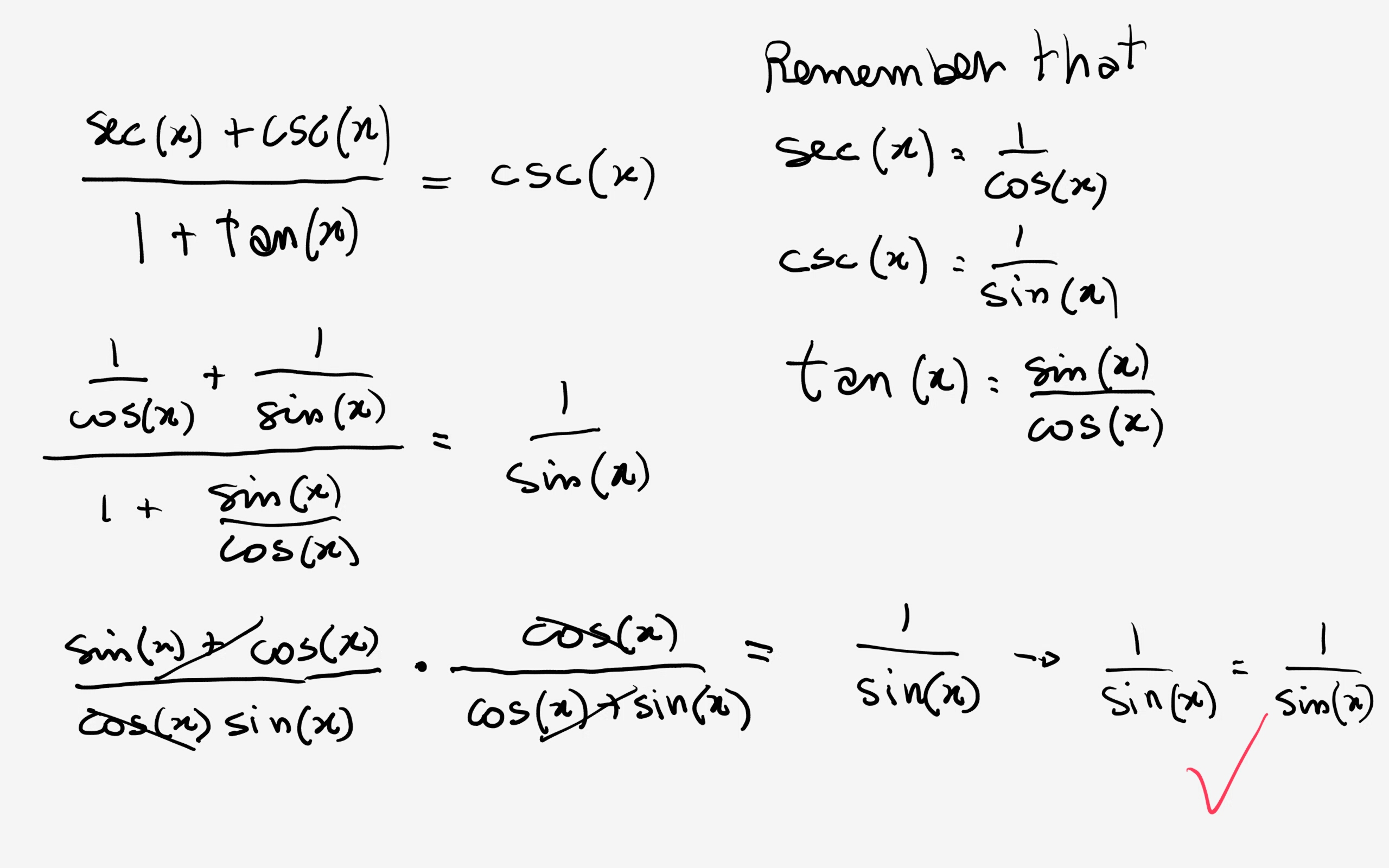



How Do You Prove Sec X Csc X 1 Tan X Csc X Socratic



Http Chesshir Weebly Com Uploads 8 6 7 9 Chapter 5 Trigonometric Identities And Equations Pdf



Q Tbn And9gctg1mv4zqwzzx9es1vyuwisok4cikumrujuyo2nyqlvyw5qkqqv Usqp Cau
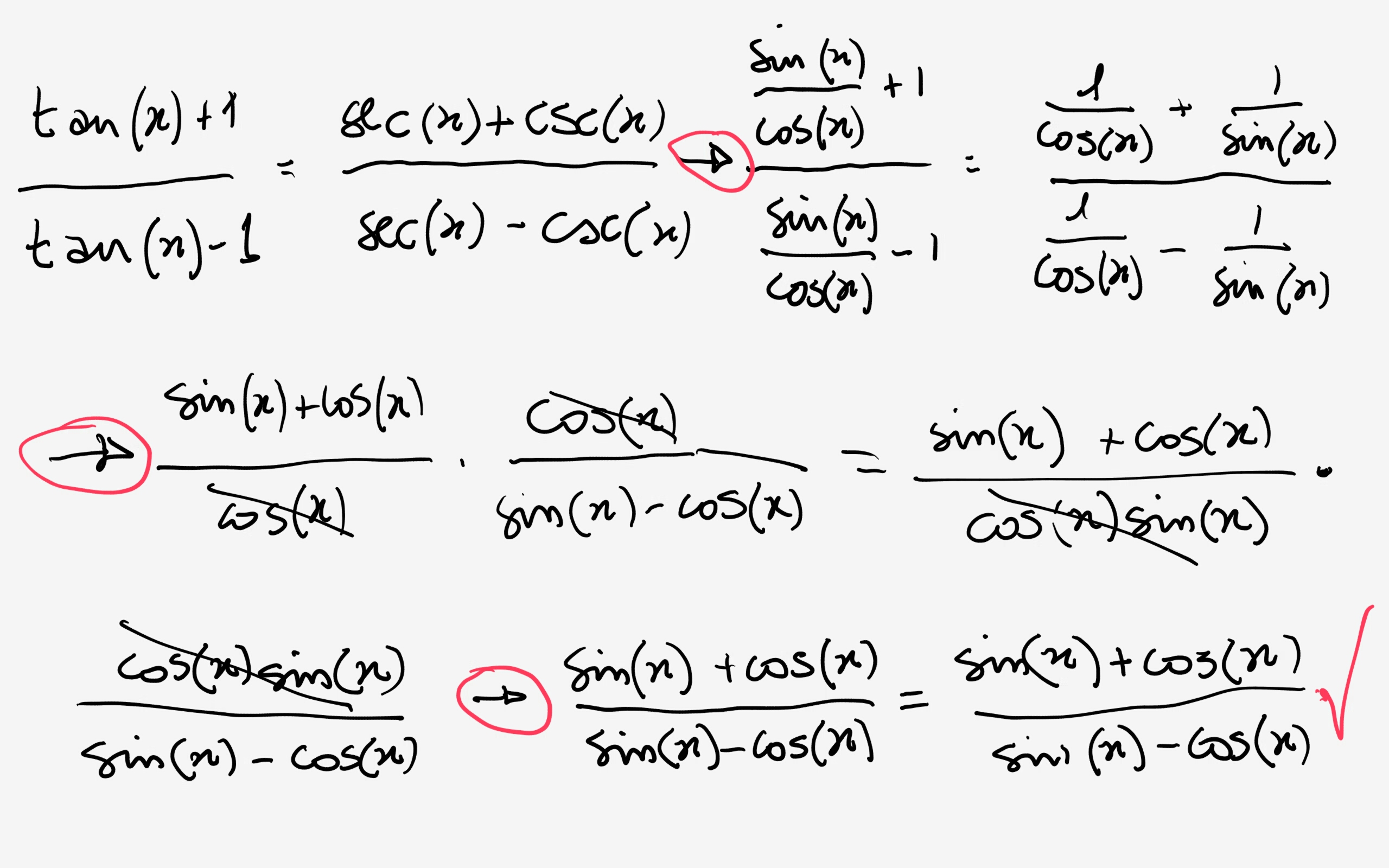



How Do You Prove Tan X 1 Tan X 1 Sec X Csc X Sec X Csc X Socratic



Http Www Math Tamu Edu Snite 150lect7 1 Pdf



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿